Overview – Acupuncture is part of a family of procedures involving the stimulation of specific anatomical locations on the skin/body by a variety of techniques. There are a number of different approaches to diagnosis and treatment in North American acupuncture that incorporate traditions from China, Japan, Korea and other Asian countries. The most thoroughly studied mechanism of stimulation of acupuncture points, employs the penetration of the skin by filiform needles, which may then be manipulated manually or by electrical stimulation.
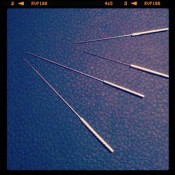 Acupuncture: is the procedure of inserting very thin disposable filiform needles into specific acupuncture points in the skin to relieve pain or for therapeutic purposes. The points selected, aid in correcting imbalances in the flow of Qi through channels known as meridians (energy pathways).
Acupuncture: is the procedure of inserting very thin disposable filiform needles into specific acupuncture points in the skin to relieve pain or for therapeutic purposes. The points selected, aid in correcting imbalances in the flow of Qi through channels known as meridians (energy pathways).
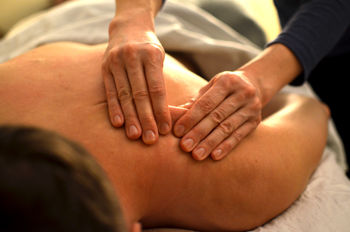 Tui Na (Chinese Massage): is a Chinese manipulative massage therapy, (directly translated as ‘push-grasp’), whose purpose is to regulate the functions of internal organs, harmonize the circulation of Qi and blood, and to help one recover from musculoskeletal injuries. It is a hands-on body treatment that is a modality of Chinese medicine whose purpose is to bring the body into balance.
Tui Na (Chinese Massage): is a Chinese manipulative massage therapy, (directly translated as ‘push-grasp’), whose purpose is to regulate the functions of internal organs, harmonize the circulation of Qi and blood, and to help one recover from musculoskeletal injuries. It is a hands-on body treatment that is a modality of Chinese medicine whose purpose is to bring the body into balance.
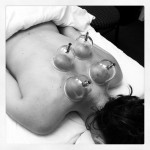 Cupping: is a safe, non-invasive technique which practitioners use to treat a myriad of conditions, such as colds & flu, upper respiratory infections, problems of the internal organs, and muscular tension. In modern practice, this involves the application of plastic cups to specific areas of the body which then a hand-held suction device is used to pump air from within the cup. This causes the skin to be sucked up into the cup, stimulating the flow of Qi and blood and aiding in clearing local stagnation. (Traditionally, the suction procedure is done using glass cups and a small flame held inside in order to create a small vacuum.)
Cupping: is a safe, non-invasive technique which practitioners use to treat a myriad of conditions, such as colds & flu, upper respiratory infections, problems of the internal organs, and muscular tension. In modern practice, this involves the application of plastic cups to specific areas of the body which then a hand-held suction device is used to pump air from within the cup. This causes the skin to be sucked up into the cup, stimulating the flow of Qi and blood and aiding in clearing local stagnation. (Traditionally, the suction procedure is done using glass cups and a small flame held inside in order to create a small vacuum.)
 Moxibustion (Moxa): is the use of herbs burned in order to warm regions and acupuncture points. (This may be carried out either ‘above the skin’, ‘on the tip of the handle’ of the acupuncture needle that has been inserted into the skin, or ‘directly on the skin’). This technique stimulates the circulation through the points and promotes the smooth flow of blood and energy. Moxibustion may be used separately or as an accompaniment to acupuncture treatment.
Moxibustion (Moxa): is the use of herbs burned in order to warm regions and acupuncture points. (This may be carried out either ‘above the skin’, ‘on the tip of the handle’ of the acupuncture needle that has been inserted into the skin, or ‘directly on the skin’). This technique stimulates the circulation through the points and promotes the smooth flow of blood and energy. Moxibustion may be used separately or as an accompaniment to acupuncture treatment.
G ua Sha (Scraping): is an ancient therapy practiced in traditional Chinese medicine that is used to relieve the stagnation of blood that obstructs surface tissues and inhibits organ function. The meaning of ‘Gua’ is to rub or to scrape, while ‘Sha’ means a reddish and raised area of skin. First, therapeutic oil is applied to the skin to act as a lubricating medium, then the technique is facilitated by repeated pressing and scraping specific areas of the skin with blunt edged device, resulting in the appearance of red, elevated patches on the treated area. Gua Sha is particularly effective in relieving body pain from headaches to shoulder, neck, back and joint pains as well as rheumatism. Gua Sha is helpful for improving circulation, regulating organ functions, relieving pain and revitalizing Qi.
ua Sha (Scraping): is an ancient therapy practiced in traditional Chinese medicine that is used to relieve the stagnation of blood that obstructs surface tissues and inhibits organ function. The meaning of ‘Gua’ is to rub or to scrape, while ‘Sha’ means a reddish and raised area of skin. First, therapeutic oil is applied to the skin to act as a lubricating medium, then the technique is facilitated by repeated pressing and scraping specific areas of the skin with blunt edged device, resulting in the appearance of red, elevated patches on the treated area. Gua Sha is particularly effective in relieving body pain from headaches to shoulder, neck, back and joint pains as well as rheumatism. Gua Sha is helpful for improving circulation, regulating organ functions, relieving pain and revitalizing Qi.

